
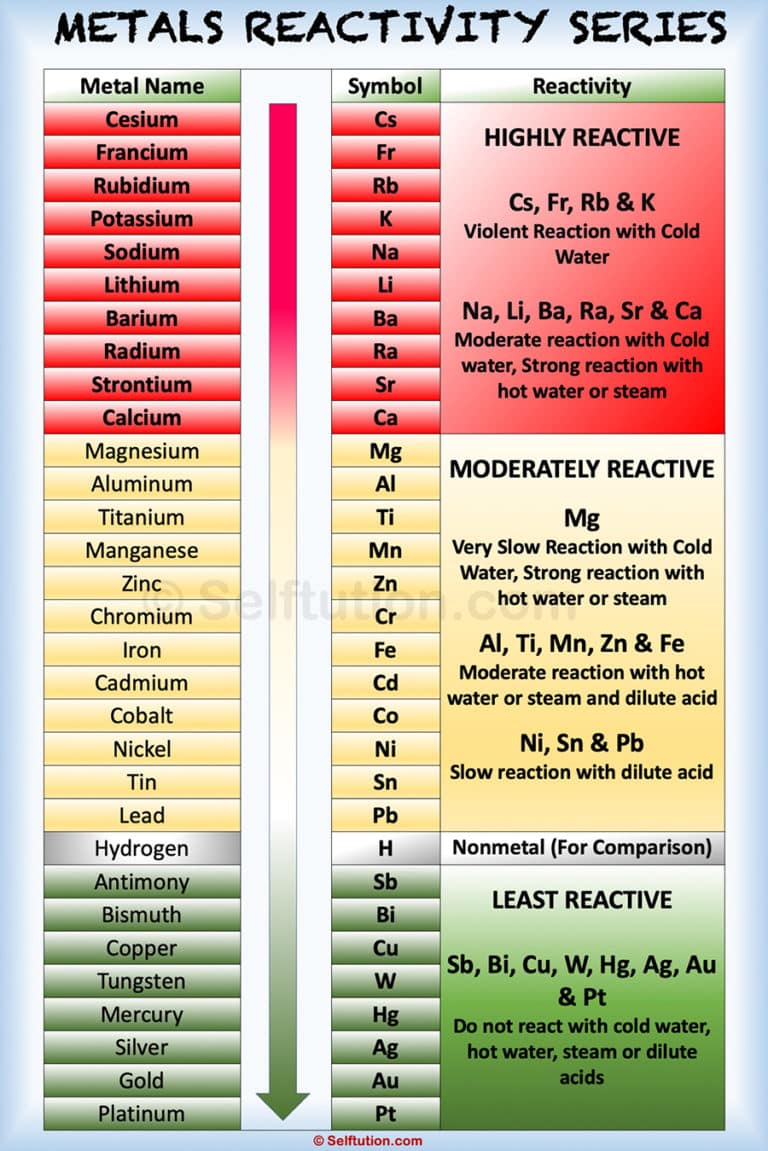
The activity series is often represented as a list, with the most active elements at the top and the least active elements at the bottom. More active elements are able to more readily lose electrons and form cations, while less active elements are less likely to do so.Įlements that are more likely to lose electrons and form cations are higher up in the activity series, while elements that are less likely to lose electrons and form cations are lower down in the activity series.

The activity of an element is determined by its ability to lose electrons and form positive ions, or cations. It is used to predict the products of single replacement reactions, in which one element is replaced by another element in a compound. The activity series is a list of elements arranged in order of their relative reactivity. What is known as activity series?Īn activity series is a list of elements arranged in order of their relative reactivity. The activity series is often used in chemistry to predict the products of a chemical reaction and to determine which elements will be oxidized or reduced in a reaction. The activity series is based on the idea that some elements are more reactive than others, and that the reactivity of an element can be predicted by its position in the series. The activity of an element is a measure of its tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and the activity series is used to predict how elements will behave in a chemical reaction. The activity series is a useful tool for predicting the products of redox reactions, but it should be used with caution, as other factors such as the nature of the reactants and the presence of catalysts can affect the outcome of a reaction. The position of a metal on the activity series is determined by its standard reduction potential, which is a measure of the tendency of a metal to gain or lose electrons. It’s important to note that the activity series is not a fixed list and can vary depending on the specific conditions of a reaction. Here is a list of common metals in the activity series, from most active (most likely to lose electrons) to least active (least likely to lose electrons): The activity series can also be used to predict the products of reactions between metals and their compounds. The activity series is used to predict the products of displacement reactions and to identify the more reactive element in a redox reaction. The activity of a metal can be determined by its tendency to form a positive ion (cation) by losing electrons to a nonmetal. The activity series of metals is a list of metals arranged in order of decreasing ease of oxidation, or the ability to lose electrons. In the example above, the copper(II) sulfate is the oxidizing agent and the zinc is the reducing agent The oxidizing agent is the element that is being reduced (gaining electrons) and the reducing agent is the element that is being oxidized (losing electrons). The activity series can also be used to identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent in a redox reaction. The reaction can be represented by the following equation: For example, if zinc metal is placed in a solution of copper(II) sulfate, the zinc will displace the copper and form zinc sulfate, because zinc is higher in the activity series than copper. The activity series can be used to predict the products of single displacement reactions, where one element is replaced by another element in a compound.

On the other hand, platinum is the least reactive element on the list and is less likely to lose electrons and be oxidized. This means that potassium is the most reactive element on the list and is more likely to lose electrons and be oxidized. Potassium > Sodium > Calcium > Magnesium > Aluminum > Zinc > Iron > Nickel > Tin > Lead > Hydrogen > Copper > Silver > Gold > Platinum The most reactive elements are at the top of the activity series, while the least reactive elements are at the bottom.įor example, the activity series for some common elements is: The activity series is based on the observation that some elements are more likely to lose electrons and be oxidized (become positive ions) while others are more likely to gain electrons and be reduced (become negative ions). It is used to predict the products of single displacement reactions and to help identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent in a redox reaction. The activity series is a list of elements in order of their relative reactivity. Is activity series only for single replacement?.What is the correct order of activity series?.Does the activity series apply to double replacement reactions?.

An element in the activity series can replace any element.When should you use the activity series?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
